UK Economy Sees Modest Growth Amidst Sectoral Challenges
Published 12 February 2026
Highlights
- The UK economy grew by 0.1% in the last quarter of 2025, slightly below the expected 0.2%.
- The services sector, which constitutes 80% of the economy, showed no growth, while manufacturing provided the main boost.
- Construction activity fell by 2.1%, marking its worst performance in over four years.
- The Bank of England has lowered its growth forecast for 2026 and expects unemployment to rise to 5.3%.
- Chancellor Rachel Reeves claims the government's economic plan is effective, but critics argue it has stifled recovery.
-
Rewritten Article
UK Economy Sees Modest Growth Amidst Sectoral Challenges
The UK economy experienced a modest growth of 0.1% in the final quarter of 2025, according to the Office for National Statistics (ONS). This slight increase fell short of economists' expectations of a 0.2% rise, highlighting ongoing challenges within key sectors.
Sectoral Performance and Economic Drivers
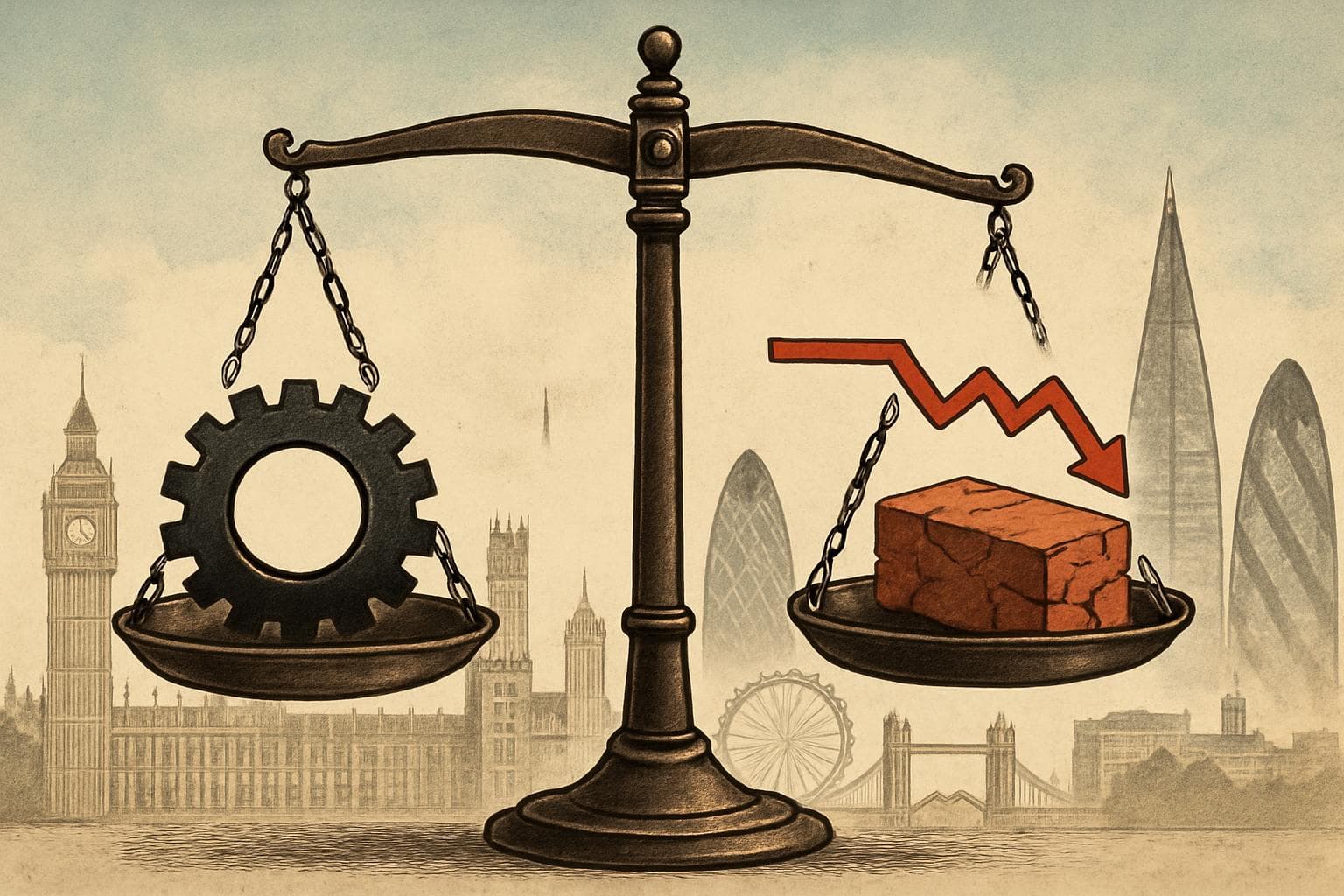
The services sector, which accounts for approximately 80% of the UK economy, stagnated during this period, marking the first instance of no growth in two years. In contrast, manufacturing emerged as a key driver, contributing significantly to the overall economic performance. However, the construction industry faced a downturn, with activity declining by 2.1%, the worst in over four years, due to reduced repair and maintenance work and fewer new projects.
Liz McKeown, director of economic statistics at the ONS, described the overall economic picture as one of "subdued growth." The economy's annual growth rate for 2025 was 1.3%, a slight improvement from 1.1% in 2024, yet still below the Bank of England's forecast of 1.4%.
Political and Economic Reactions
Chancellor Rachel Reeves defended the government's economic strategy, asserting that it has laid the groundwork for potential interest rate cuts by the Bank of England. "The government has the right economic plan to build a stronger and more secure economy," Reeves stated. However, critics, including shadow chancellor Sir Mel Stride, argue that the government's approach has weakened the economy, with the Liberal Democrats criticizing Reeves' budgets for stifling recovery.
The Bank of England recently adjusted its economic forecasts, predicting a growth rate of 0.9% for 2026, down from an earlier estimate of 1.2%. Additionally, the unemployment rate is expected to rise to 5.3%, up from the initial forecast of 5%.
Impact of External Factors
The UK's economic performance in 2025 was also affected by external factors, such as a cyber-attack on Jaguar Land Rover, which disrupted vehicle production and contributed to minimal growth in the third quarter. Despite these challenges, the economy managed to grow by 0.7% in the first quarter and 0.3% in the second quarter of the year.
-
Scenario Analysis
Looking ahead, the UK's economic trajectory remains uncertain. The Bank of England's decision to keep interest rates unchanged at 3.75% reflects a cautious approach amidst mixed economic signals. Should inflation continue to decline, as anticipated due to cost-of-living measures in Reeves's budget, there may be room for interest rate cuts in the coming months.
Politically, the Labour government faces pressure to demonstrate the effectiveness of its economic policies. As Chancellor Reeves seeks to strengthen ties with the EU, the government's ability to foster growth and investment will be crucial in shaping public perception and political fortunes.
Experts suggest that addressing sector-specific challenges, particularly in construction and services, will be vital for sustaining economic momentum. The government's response to these issues, alongside broader economic policies, will likely influence the UK's economic outlook in the near future.
The UK economy experienced a modest growth of 0.1% in the final quarter of 2025, according to the Office for National Statistics (ONS). This slight increase fell short of economists' expectations of a 0.2% rise, highlighting ongoing challenges within key sectors.
Sectoral Performance and Economic Drivers
The services sector, which accounts for approximately 80% of the UK economy, stagnated during this period, marking the first instance of no growth in two years. In contrast, manufacturing emerged as a key driver, contributing significantly to the overall economic performance. However, the construction industry faced a downturn, with activity declining by 2.1%, the worst in over four years, due to reduced repair and maintenance work and fewer new projects.
Liz McKeown, director of economic statistics at the ONS, described the overall economic picture as one of "subdued growth." The economy's annual growth rate for 2025 was 1.3%, a slight improvement from 1.1% in 2024, yet still below the Bank of England's forecast of 1.4%.
Political and Economic Reactions
Chancellor Rachel Reeves defended the government's economic strategy, asserting that it has laid the groundwork for potential interest rate cuts by the Bank of England. "The government has the right economic plan to build a stronger and more secure economy," Reeves stated. However, critics, including shadow chancellor Sir Mel Stride, argue that the government's approach has weakened the economy, with the Liberal Democrats criticizing Reeves' budgets for stifling recovery.
The Bank of England recently adjusted its economic forecasts, predicting a growth rate of 0.9% for 2026, down from an earlier estimate of 1.2%. Additionally, the unemployment rate is expected to rise to 5.3%, up from the initial forecast of 5%.
Impact of External Factors
The UK's economic performance in 2025 was also affected by external factors, such as a cyber-attack on Jaguar Land Rover, which disrupted vehicle production and contributed to minimal growth in the third quarter. Despite these challenges, the economy managed to grow by 0.7% in the first quarter and 0.3% in the second quarter of the year.
What this might mean
Looking ahead, the UK's economic trajectory remains uncertain. The Bank of England's decision to keep interest rates unchanged at 3.75% reflects a cautious approach amidst mixed economic signals. Should inflation continue to decline, as anticipated due to cost-of-living measures in Reeves's budget, there may be room for interest rate cuts in the coming months.
Politically, the Labour government faces pressure to demonstrate the effectiveness of its economic policies. As Chancellor Reeves seeks to strengthen ties with the EU, the government's ability to foster growth and investment will be crucial in shaping public perception and political fortunes.
Experts suggest that addressing sector-specific challenges, particularly in construction and services, will be vital for sustaining economic momentum. The government's response to these issues, alongside broader economic policies, will likely influence the UK's economic outlook in the near future.