US Economic Growth Slows Amid Government Shutdown and Inflation Concerns
Published 20 February 2026
Highlights
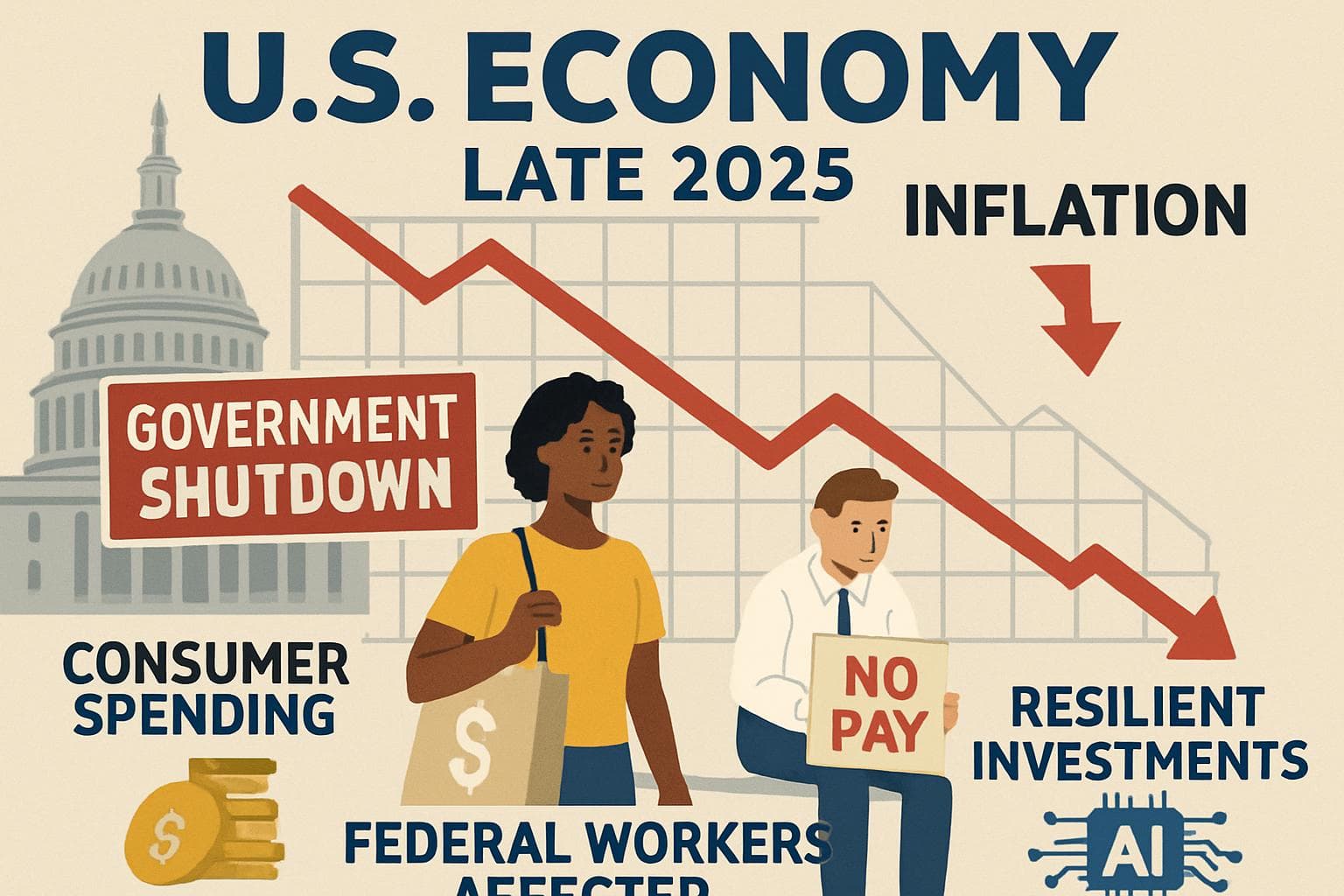
- US economic growth slowed to 1.4% in Q4 2025, down from 4.4% in Q3, largely due to a government shutdown and reduced consumer spending.
- The government shutdown subtracted an estimated 1 to 1.5 percentage points from GDP, with some losses expected to be recovered.
- Inflation, measured by the PCE price index, rose to 2.9% in December, potentially influencing Federal Reserve decisions.
- Consumer spending growth slowed to 2.4% in Q4, with higher-income households driving spending amid inflation pressures.
- Investment in artificial intelligence and tax cuts are expected to support economic activity in 2026.
The US economy experienced a significant slowdown in the final quarter of 2025, with growth decelerating to an annualized rate of 1.4%, according to the Commerce Department's Bureau of Economic Analysis. This marks a sharp decline from the robust 4.4% growth recorded in the third quarter. The slowdown was primarily attributed to the prolonged government shutdown and a moderation in consumer spending.
Impact of the Government Shutdown
The 43-day government shutdown, which ended in December, had a pronounced impact on economic activity. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimated that the shutdown reduced fourth-quarter GDP by 1 to 1.5 percentage points. This was due to fewer services provided by federal workers and a temporary reduction in government spending. While some of the lost output is expected to be recovered, the CBO projected that between $7 billion and $14 billion may not be recouped.
Consumer Spending and Inflation
Consumer spending, a key driver of the US economy, grew by 2.4% in the fourth quarter, down from 3.5% in the previous quarter. Analysts noted that spending was largely driven by higher-income households, as inflation eroded the purchasing power of lower-income consumers. The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index, a preferred measure of inflation by the Federal Reserve, rose to 2.9% in December, up from 2.8% in November. This increase in inflation could influence future monetary policy decisions by the Federal Reserve.
Investment and Future Outlook
Despite the slowdown, investment in artificial intelligence and related technologies, such as datacenters and semiconductors, provided a buffer against the economic headwinds. Economists anticipate that these investments, along with recent tax cuts, will support economic activity in 2026. Michael Pearce, chief US economist at Oxford Economics, expressed optimism, stating, "The core of the economy is resilient," and predicted a rebound in growth in the coming year.
What this might mean
Looking ahead, the US economy faces a complex landscape. The recent rise in inflation could prompt the Federal Reserve to reconsider its monetary policy stance, potentially impacting interest rates. Additionally, the anticipated recovery of lost output from the government shutdown may provide a temporary boost to growth. However, the ongoing affordability crisis, driven by high inflation and stagnant wage growth, poses a challenge for lower-income households. As the economy navigates these uncertainties, the role of technological investments and fiscal policies will be crucial in shaping the trajectory of US economic growth in 2026 and beyond.