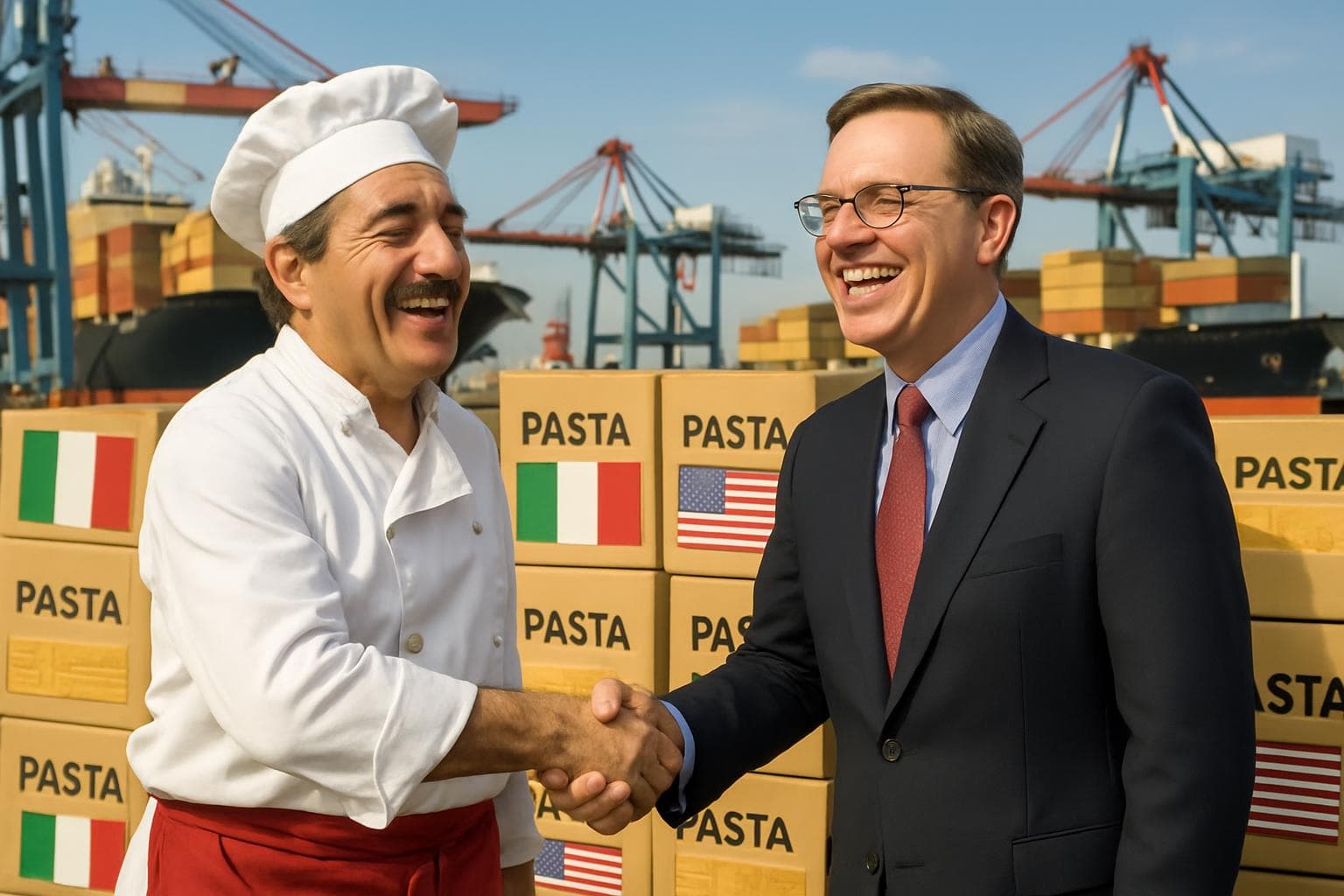
US Reduces Proposed Tariffs on Italian Pasta Imports
Published 2 January 2026
Highlights
- The US has significantly reduced proposed tariffs on Italian pasta imports, initially set at nearly 92%.
- The revised tariffs now range from 2% to 14%, following cooperation from Italian pasta producers.
- The US Department of Commerce will finalize the tariff decision on March 12, after further analysis.
- The tariffs affect 13 Italian companies, which account for about 16% of pasta imports to the US.
- The European Commission has indicated it may intervene if necessary, highlighting the international trade implications.
-
Rewritten Article
US Reduces Proposed Tariffs on Italian Pasta Imports
In a significant development for international trade, the United States has decided to drastically reduce the proposed tariffs on Italian pasta imports, which were initially set to reach nearly 92%. This decision comes after the Trump administration accused 13 Italian pasta producers, including well-known brands like Barilla and La Molisana, of selling their products at unfairly low prices in the US market.
Background and Initial Tariff Proposal
The initial proposal by the US Department of Commerce aimed to impose tariffs that would have nearly doubled the cost of Italian pasta for American consumers. This move was part of a broader strategy by the Trump administration to address trade practices perceived as harmful to US interests and to bolster American manufacturing. The proposed tariffs were set to be as high as 91.74%, which, when combined with an existing 15% tariff on most European Union imports, would have resulted in a tax rate exceeding 100% of the pasta's value.
Revised Tariff Rates and Industry Response
On Thursday, the Italian foreign ministry announced that the US had revised the proposed tariffs to a range between 2% and 14%. This adjustment followed a preliminary analysis by the US Department of Commerce, which acknowledged that Italian pasta makers had addressed many of the concerns raised. The recalculated tariffs are seen as a recognition of the constructive cooperation shown by the Italian companies.
Impact and Future Considerations
The 13 targeted companies represent approximately 16% of Italian pasta imports to the US, with Italy responsible for an estimated $770 million in annual pasta sales to the country. The European Commission has expressed readiness to intervene if necessary, underscoring the broader implications for EU-US trade relations. The final decision on the import duties will be announced on March 12, following further analysis by the US Department of Commerce.
Broader Trade Context
This development occurs amid a series of tariff adjustments by the US, including a recent delay in planned increases on imports of furniture items. The White House has indicated ongoing negotiations with trade partners, reflecting a complex landscape of international trade dynamics.
-
Scenario Analysis
The reduction in proposed tariffs on Italian pasta imports marks a potential easing of trade tensions between the US and the European Union. If the final decision on March 12 confirms the lower tariff rates, it could pave the way for improved trade relations and set a precedent for resolving similar disputes. However, should the tariffs be reinstated at higher levels, it may prompt intervention from the European Commission and further complicate EU-US trade negotiations. Experts suggest that the outcome will significantly influence future trade policies and the global economic landscape.
In a significant development for international trade, the United States has decided to drastically reduce the proposed tariffs on Italian pasta imports, which were initially set to reach nearly 92%. This decision comes after the Trump administration accused 13 Italian pasta producers, including well-known brands like Barilla and La Molisana, of selling their products at unfairly low prices in the US market.
Background and Initial Tariff Proposal
The initial proposal by the US Department of Commerce aimed to impose tariffs that would have nearly doubled the cost of Italian pasta for American consumers. This move was part of a broader strategy by the Trump administration to address trade practices perceived as harmful to US interests and to bolster American manufacturing. The proposed tariffs were set to be as high as 91.74%, which, when combined with an existing 15% tariff on most European Union imports, would have resulted in a tax rate exceeding 100% of the pasta's value.
Revised Tariff Rates and Industry Response
On Thursday, the Italian foreign ministry announced that the US had revised the proposed tariffs to a range between 2% and 14%. This adjustment followed a preliminary analysis by the US Department of Commerce, which acknowledged that Italian pasta makers had addressed many of the concerns raised. The recalculated tariffs are seen as a recognition of the constructive cooperation shown by the Italian companies.
Impact and Future Considerations
The 13 targeted companies represent approximately 16% of Italian pasta imports to the US, with Italy responsible for an estimated $770 million in annual pasta sales to the country. The European Commission has expressed readiness to intervene if necessary, underscoring the broader implications for EU-US trade relations. The final decision on the import duties will be announced on March 12, following further analysis by the US Department of Commerce.
Broader Trade Context
This development occurs amid a series of tariff adjustments by the US, including a recent delay in planned increases on imports of furniture items. The White House has indicated ongoing negotiations with trade partners, reflecting a complex landscape of international trade dynamics.
What this might mean
The reduction in proposed tariffs on Italian pasta imports marks a potential easing of trade tensions between the US and the European Union. If the final decision on March 12 confirms the lower tariff rates, it could pave the way for improved trade relations and set a precedent for resolving similar disputes. However, should the tariffs be reinstated at higher levels, it may prompt intervention from the European Commission and further complicate EU-US trade negotiations. Experts suggest that the outcome will significantly influence future trade policies and the global economic landscape.