US Inflation Eases to 2.4% Amidst Tariff and Economic Uncertainties
Published 13 February 2026
Highlights
- US inflation eased to 2.4% in January, marking the slowest pace since May, as energy and used car prices fell.
- The Federal Reserve may consider interest rate cuts, though analysts warn of potential inflationary pressures from tariffs and labor shortages.
- President Trump celebrated the inflation report, claiming it as a victory over economic challenges and a boost for the US economy.
- Core CPI, excluding food and energy, rose by 0.3% in January, with notable increases in personal services and other sectors.
- Recent polls indicate voter dissatisfaction with Trump's economic management, particularly regarding inflation and tariffs.
-
Rewritten Article
US Inflation Eases to 2.4% Amidst Tariff and Economic Uncertainties
Inflation in the United States cooled to 2.4% in January, the slowest pace since May, as prices for energy and used cars declined, according to the Department of Labor. This development has sparked discussions about potential interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve, although some analysts caution that inflationary pressures could resurface due to tariffs and labor shortages.
Economic Indicators and Federal Reserve's Stance
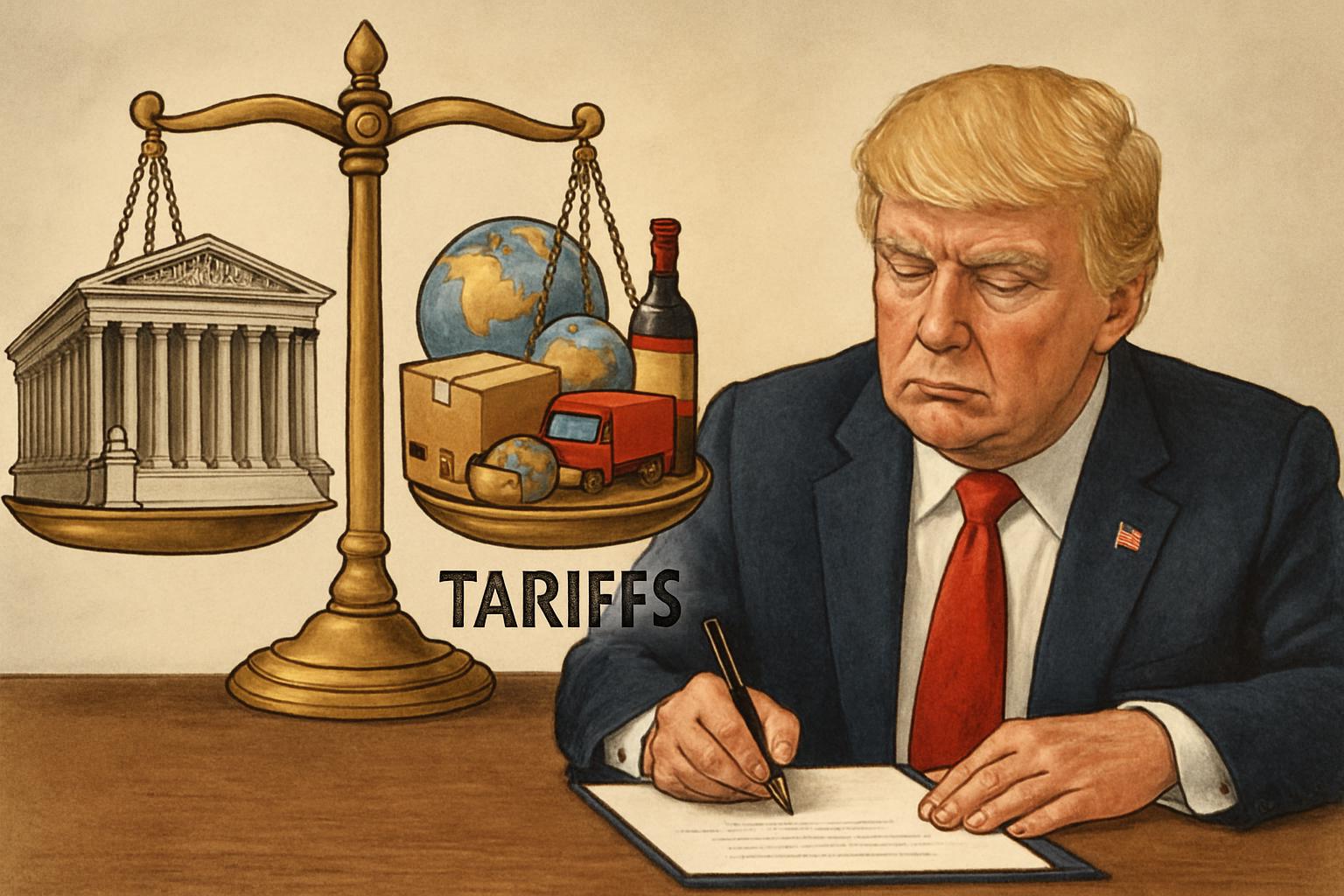
The consumer price index (CPI) rose by 0.2% from December to January, while the core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, increased by 0.3%. These figures suggest a moderation in inflation, providing the Federal Reserve with room to maneuver. Neil Birrell, chief investment officer at Premier Miton Investors, noted that the January report might ease the path towards a rate cut. However, he warned that tariffs and labor market constraints could still impact inflation.
Political Reactions and Economic Implications
President Donald Trump and the White House were quick to celebrate the inflation report, framing it as evidence of the success of Trump's economic policies. "The US economy is unbelievable," Trump stated, emphasizing the potential for further economic growth with interest rate cuts. However, recent polls reveal voter dissatisfaction with Trump's handling of the economy, particularly concerning inflation and tariffs.
Market and Labor Market Dynamics
The Federal Reserve, led by Chair Jerome Powell, is closely monitoring the situation. Powell acknowledged that tariffs are still influencing the economy but expects their impact to stabilize over time. Meanwhile, the labor market showed signs of strength in January, although job growth figures for 2025 were revised downward. This mixed economic landscape presents challenges for policymakers as they navigate interest rate decisions.
-
Scenario Analysis
Looking ahead, the Federal Reserve's decisions on interest rates will be pivotal in shaping the US economic landscape. While the current inflation data provides some leeway for potential rate cuts, the lingering effects of tariffs and labor market dynamics could complicate this trajectory. Economists will be watching closely for any signs of inflationary pressures that might prompt a reevaluation of monetary policy.
Politically, the Trump administration faces mounting pressure as voter dissatisfaction grows, particularly with the midterm elections approaching. The administration's focus on tariffs and immigration has left some voters uneasy, potentially impacting Republican prospects in upcoming elections. As the economic narrative unfolds, both the Federal Reserve and the White House will need to carefully balance their strategies to maintain economic stability and voter confidence.
Inflation in the United States cooled to 2.4% in January, the slowest pace since May, as prices for energy and used cars declined, according to the Department of Labor. This development has sparked discussions about potential interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve, although some analysts caution that inflationary pressures could resurface due to tariffs and labor shortages.
Economic Indicators and Federal Reserve's Stance
The consumer price index (CPI) rose by 0.2% from December to January, while the core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, increased by 0.3%. These figures suggest a moderation in inflation, providing the Federal Reserve with room to maneuver. Neil Birrell, chief investment officer at Premier Miton Investors, noted that the January report might ease the path towards a rate cut. However, he warned that tariffs and labor market constraints could still impact inflation.
Political Reactions and Economic Implications
President Donald Trump and the White House were quick to celebrate the inflation report, framing it as evidence of the success of Trump's economic policies. "The US economy is unbelievable," Trump stated, emphasizing the potential for further economic growth with interest rate cuts. However, recent polls reveal voter dissatisfaction with Trump's handling of the economy, particularly concerning inflation and tariffs.
Market and Labor Market Dynamics
The Federal Reserve, led by Chair Jerome Powell, is closely monitoring the situation. Powell acknowledged that tariffs are still influencing the economy but expects their impact to stabilize over time. Meanwhile, the labor market showed signs of strength in January, although job growth figures for 2025 were revised downward. This mixed economic landscape presents challenges for policymakers as they navigate interest rate decisions.
What this might mean
Looking ahead, the Federal Reserve's decisions on interest rates will be pivotal in shaping the US economic landscape. While the current inflation data provides some leeway for potential rate cuts, the lingering effects of tariffs and labor market dynamics could complicate this trajectory. Economists will be watching closely for any signs of inflationary pressures that might prompt a reevaluation of monetary policy.
Politically, the Trump administration faces mounting pressure as voter dissatisfaction grows, particularly with the midterm elections approaching. The administration's focus on tariffs and immigration has left some voters uneasy, potentially impacting Republican prospects in upcoming elections. As the economic narrative unfolds, both the Federal Reserve and the White House will need to carefully balance their strategies to maintain economic stability and voter confidence.