US Inflation Steady as Tariffs Begin to Impact Consumer Prices
Published 12 August 2025
Highlights
- US inflation remained at 2.7% in July, with core inflation rising to 3.1%, the fastest pace since February.
- The Federal Reserve faces pressure to cut interest rates amid economic uncertainty and President Trump's tariff policies.
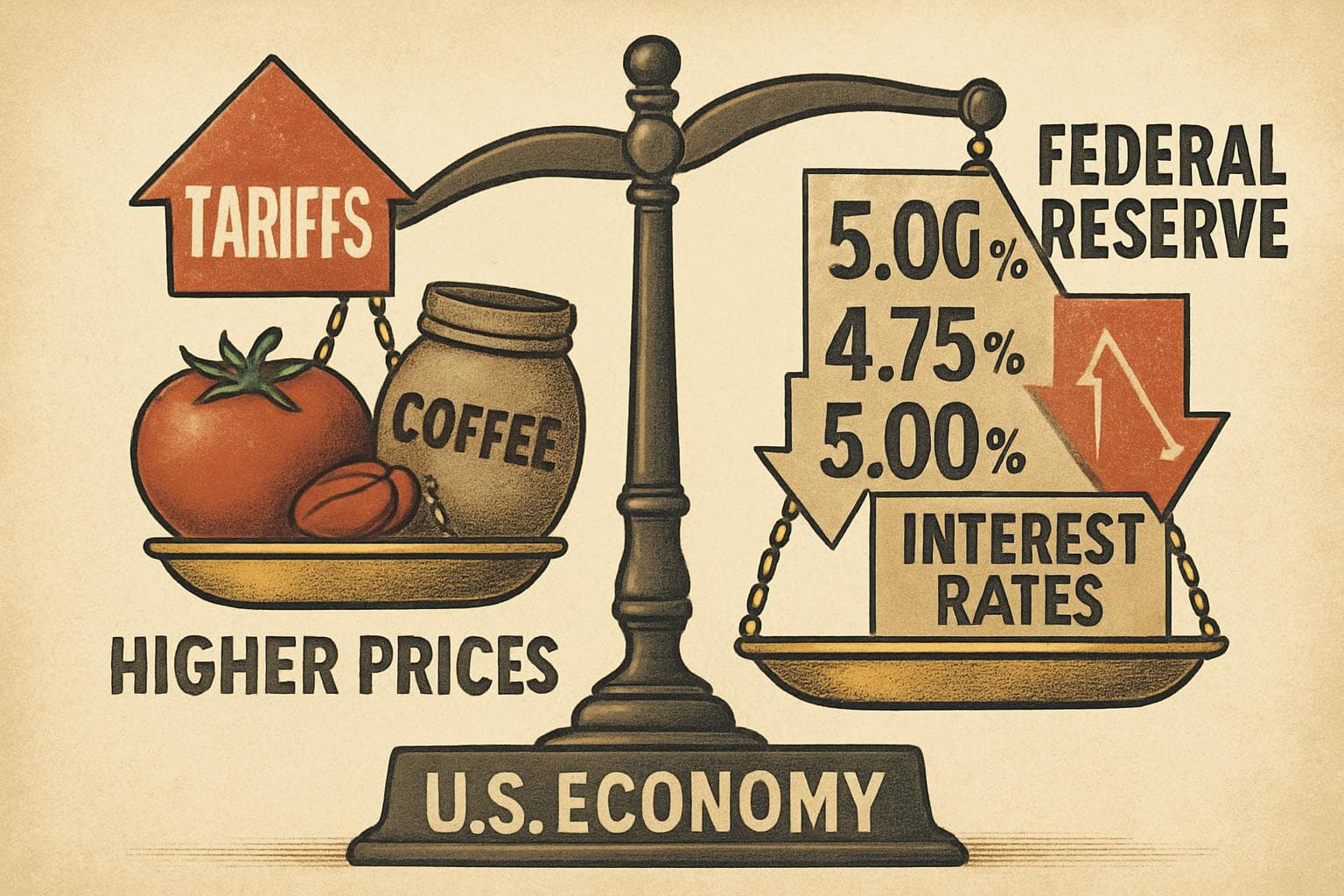
- Tariffs have begun impacting consumer prices, with notable increases in items like tomatoes and coffee.
- President Trump has criticized the Federal Reserve and fired the head of the Bureau of Labor Statistics over economic data disputes.
- Economists warn that tariffs could further affect prices and the labor market, complicating the Fed's policy decisions.
In July, US inflation held steady at 2.7%, according to official figures, as the effects of President Donald Trump's tariffs began to influence consumer costs. Despite the stable inflation rate, core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, rose to 3.1%, marking the fastest increase since February. This development has intensified the debate over the Federal Reserve's next move on interest rates.
Tariffs and Consumer Prices
The latest data reveal that while overall energy prices have decreased by 1.6% over the past year, consumer prices for goods such as tomatoes and coffee have risen by 3.3% and 2.3%, respectively. These increases are attributed to the tariffs imposed by the Trump administration, which include a 10% universal tariff on imports and higher tariffs on specific industries like steel and aluminum. Although many tariffs only took effect in early August, companies have started passing on these costs to consumers, as predicted by major retailers like Walmart and Nike.
Federal Reserve Under Pressure
The Federal Reserve, which aims to maintain inflation at 2%, is under mounting pressure to cut interest rates to support the economy. Seema Shah, chief global strategist at Principal Asset Management, anticipates a rate cut in September to boost economic growth. However, the decision is complicated by the potential for tariffs to further drive up prices. President Trump has been vocal in his criticism of the Fed, urging a reduction in borrowing costs and threatening legal action against Fed Chair Jerome Powell.
Economic and Political Tensions
The economic landscape is further strained by a revision in job figures, which showed a significant decrease from the initially reported 291,000 jobs added in May and June to just 33,000. This has fueled concerns about the labor market's resilience amid the tariff-induced turbulence. Trump's dissatisfaction with economic data led to the dismissal of Erika McEntarfer, head of the Bureau of Labor Statistics, following a report of weaker-than-expected job growth.
What this might mean
Looking ahead, the Federal Reserve faces a challenging decision on whether to cut interest rates in response to the mixed economic signals. A rate cut could stimulate growth but may also risk exacerbating inflation if tariffs continue to push prices higher. Economists caution that the full impact of tariffs on consumer prices and the labor market may not yet be fully realized, potentially complicating future policy decisions. As negotiations with China continue, the outcome could significantly influence the trajectory of US economic policy and the global trading landscape.